Exploring the Impact of AI on Society: Innovations, Concerns, and the Future
Author: Ayushi Jain
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved and integrated itself into various aspects of daily life, from personal assistants like Siri and Alexa to sophisticated analytics tools utilized in business. This transformative technology has sparked discussions about its implications for productivity, employment, privacy, and societal norms.
One of the most significant advancements in AI is the introduction of generative models that can create text, images, and even music akin to human-like creativity. Companies such as Google and OpenAI have pioneered these innovations, leading to practical applications ranging from content creation to automated customer service, thus enhancing efficiency in business operations.

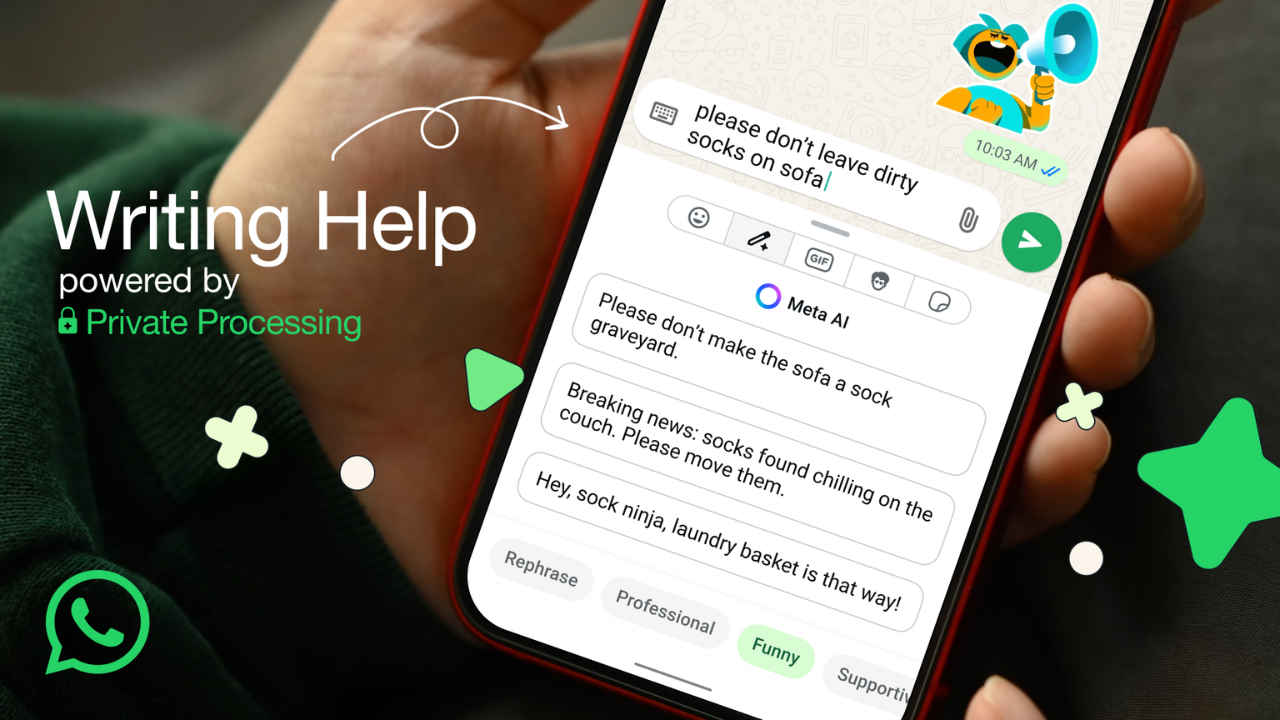
An illustration of WhatsApp's new AI feature designed to polish messages.
Despite the benefits, there are growing concerns over the ethical implications of AI. Issues like data privacy, the potential for bias in AI systems, and the risk of job displacement due to automation are at the forefront of debates among lawmakers, technologists, and ethicists alike. These discussions have prompted organizations like the TUC (Trades Union Congress) to advocate for worker-centric strategies in AI innovation to safeguard employment and ensure fair practices.
In one compelling case, AI chatbots have been scrutinized for their handling of sensitive topics such as mental health. A recent study highlighted that popular chatbots inadequately respond to suicide-related inquiries, prompting calls for improvements in how they engage with users on high-risk issues. This has raised alarm among families and mental health advocates, emphasizing the need for responsible AI development that prioritizes user safety.
As AI continues to permeate various industries, it is vital to strike a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility. For instance, initiatives like Synkka's AI workforce aim to reduce operational costs in parcel delivery while relying on advanced technologies to automate tasks previously done by humans. Such developments underscore the dual-edged nature of AI: while it drives efficiency, it also disrupts traditional employment models.
Governments and corporations are urged to collaborate in creating regulatory frameworks that not only encourage innovation but also protect the interests of society. The rollout of AI-powered tools must involve dialogues with stakeholders to address fears and ensure that AI advancements lead to equitable outcomes for all.
In conclusion, the trajectory of AI development requires a thoughtful approach that emphasizes both innovation and ethical standards. As businesses and individuals adapt to these changes, fostering an environment where technology serves humanity's best interests will be crucial for sustainable growth and trust in AI.