AI at Scale: How a Wave of 2025 Announcements Reveal AI-Powered Transformation Across Finance, Mobility, Health, and Security
Author: Editorial Team
AI is not merely a buzzword; it is increasingly presenting itself as the operating system of modern industry. A wave of announcements around mid-September 2025 demonstrates how AI-powered decisioning, optimization, and intelligent edge solutions are reshaping finance, automotive, health care, manufacturing, and security. From Swisscard AECS GmbH expanding its use of FICO Platform decisioning to optimize credit limits and onboarding, to Volkswagen Group-backed electric motorcycles showcasing rapid charging with solid-state tech, the market is moving from pilots to scalable, data-driven strategies. This trend is underpinned by a broader push to turn complex data into timely, compliant, and customer-centric actions that can be deployed across thousands—or millions—of customer interactions.
In the fintech space, Swisscard AECS GmbH, a leading premium card issuer in Switzerland, has extended its cooperation with the FICO Platform to enhance AI-powered decision optimization. Swisscard already relies on FICO for onboarding and credit limit management, and the latest enhancement promises greater flexibility in setting spending limits while simultaneously managing risk based on behavioral signals. In practice, this means more personalized credit experiences for cardholders without sacrificing risk controls, as real-time patterns in spending, repayment history, and external data—such as macroeconomic indicators—inform dynamic limit adjustments. The arrangement illustrates a broader industry shift: moving from rule-based lending to adaptive, data-driven decisioning that can respond to evolving customer behavior. As regulators intensify scrutiny of credit decisions, the ability to demonstrate transparent, explainable optimization will also become a differentiator for banks and issuers.

Global AI market outlook: AI-powered decisioning and optimization driving smarter business choices across fintech, manufacturing, and health.
The mobility and automotive sector is rapidly embracing AI-driven performance and efficiency gains, not only in the design of vehicles but in the way charging, battery technology, and vehicle integration are managed. A standout example is the Ducati V21L project, Volkswagen Group’s first all-electric motorcycle, which demonstrated a 12-minute charging window from 10% to 80% using solid-state batteries from QuantumScape. This milestone is more than a novelty; it signals the potential for mission-critical EV charging workflows to be compressed dramatically for two-wheeler markets where charging infrastructure has historically lagged. While the news centers on a prototype, it aligns with VW Group’s broader electrification strategy and is likely to catalyze investment in fast charging, thermal management, and battery tech that can deliver sustained performance without compromising safety. If scaled, such charging performance could redefine riding experience, ownership costs, and the competitiveness of premium brands in emerging markets.
AI is increasingly crossing into policy and governance, prompting debates about regulation that protects the public without stifling innovation. A warning echoed in commentary about AI regulation notes that even well-intended rules can inadvertently hinder life-saving breakthroughs by creating compliance friction, slowing clinical discoveries, or delaying responsible automation. The scenario imagines 2028 as a year when AI models capable of spotting cancer earlier could be constrained by imperfect regulatory guardrails—potentially preventing faster diagnosis, better outcomes, or data-sharing that accelerates research. The key takeaway is the need for thoughtful, proportionate governance that emphasizes risk-based oversight, robust safety testing, and continuous monitoring—without blanket throttles on experimentation. The industry’s call is for regulations that are adaptive, transparent, and technology-agnostic where possible, giving innovators room to deploy beneficial AI while preserving patient privacy, safety, and ethical standards.
In the life sciences and healthcare technology sector, a growing emphasis on AI-first thinking is reshaping R&D, manufacturing, and commercialization. An article on AI-first mindsets in pharma argues that organizations should embed AI at the core of discovery, development, and operations rather than addressing it as a separate tool. The implications are broad: faster target identification with AI-driven simulations, more efficient clinical trial design with predictive analytics, and smarter pharmacovigilance and supply chain optimization through real-time data streams. Yet with opportunity comes risk—regulated environments demand rigorous validation, explainability, and patient safety. The outlook is thus a balance: pursue AI-enabled breakthroughs while maintaining robust governance, validation workflows, and cross-functional collaboration between data scientists, clinicians, and regulatory teams.

AI-first mindset in pharma: integrating AI into discovery, development, and regulatory processes.
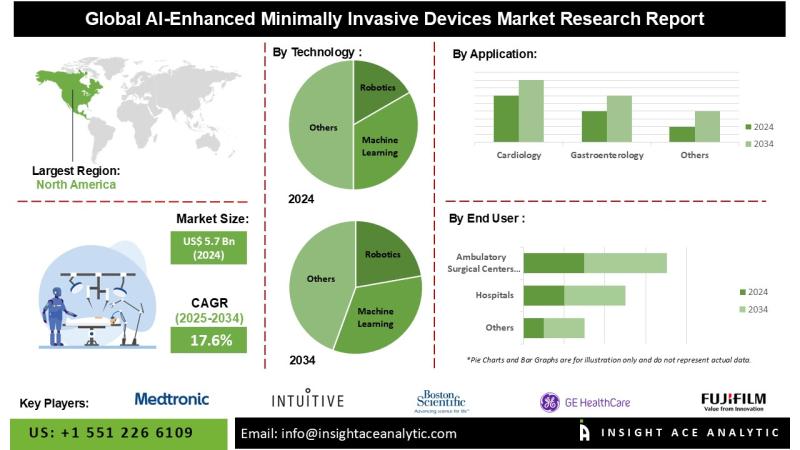
Market dynamics in medical devices are being reshaped by AI-enhanced minimally invasive technologies. An OpenPR market assessment highlights the drivers, challenges, and opportunities for AI-enabled devices such as AI-enhanced catheters, AI-powered endoscopy systems, robotic-assisted surgical platforms, and advanced imaging. The convergence of AI with minimally invasive tools promises to improve precision, reduce procedure times, and enhance patient outcomes while also expanding the addressable market for manufacturers. However, this trajectory depends on regulatory clarity, cybersecurity resilience, and interoperability standards that can harmonize AI modules with diverse imaging, sensing, and control systems across hospital settings.

AI-enabled minimally invasive devices: a growing market driven by smarter sensing, imaging, and control.
Emerging AI technologies are also accelerating capabilities in cloud and edge computing, enabling new scales of AI deployment for businesses of all sizes. Huawei’s strategic push toward high-speed AI supercomputing systems by 2027 illustrates the heavy lifting required to sustain production-grade AI workloads. Huawei’s roadmap aligns with a broader trend: enabling SMEs to access powerful AI infrastructure that previously required large, specialized data centers. The company has announced an ecosystem expansion featuring new SME Intelligence Solutions framed around 4+10+N: four core sectors, ten enabling technologies, and an open network of partners. This approach underscores a shift from bespoke, centralized AI deployments to more modular, scalable architectures that can be embedded in daily business processes, from retail to manufacturing to healthcare.

Huawei’s plan for high-speed AI compute systems and SME intelligence solutions to accelerate AI adoption in businesses of all sizes.
The AI wave is also reshaping security and surveillance ecosystems. Hikvision’s integration of AcuSeek AI-powered video analytics into its platforms HikCentral Professional and Hik-Connect 6 exemplifies how AI-driven search, recognition, and analytics are streamlining operations for organizations ranging from corporate campuses to city infrastructure. By enabling rapid video search and intelligent event detection, AI enhances incident response, operational efficiency, and safety. Yet this development raises important questions about privacy, data governance, and the responsible use of facial recognition and other sensitive indicators. The technology’s promise depends on strong privacy protections, encryption, and clear governance frameworks to prevent abuse while unlocking legitimate security benefits.

AcuSeek AI-powered video analytics integrated into HikCentral Professional and Hik-Connect 6.
The AI-enabled future is also moving into the consumer software space, where pricing models and licensing structures reflect the broader economics of AI-enabled features. A practical example is the recent reporting on Microsoft 365 pricing dynamics and the shift toward annual subscriptions for cloud services. While lifetime licenses for an older suite like Office 2021 offer a one-time cost and an offline experience, many users are now incentivized to pay ongoing subscription fees to receive continuous updates, security patches, and AI-driven productivity features. As AI becomes more embedded in everyday software—through natural language assistants, adaptive templates, and predictive analytics—the pricing question will continue to evolve. This trend will interact with enterprise licensing models, where AI-specific SKUs, usage-based billing, and flexible licensing will become commonplace.

Microsoft Office Professional 2021: a one-time license in a world moving toward AI-powered software.
The convergence of AI across devices, platforms, and sectors is not just about technological capability; it is about building ecosystems. Huawei, for example, is not simply marketing chips or software; it is constructing an ecosystem of AI-enabled hardware, cloud services, and SME-friendly infrastructure. The 4+10+N framework signals a modular, scalable approach that can adapt to the needs of diverse industries, from privacy-conscious healthcare to large-scale manufacturing and consumer services. In practice, this means providers must invest in interoperable interfaces, robust security, and transparent governance so that AI modules—from predictive maintenance to medical imaging analytics—can be plugged into existing workflows with minimal friction. The market seems to be rewarding vendors that embrace open architectures and collaborative ecosystems rather than isolated, monolithic platforms.

Huawei’s 4+10+N SME Intelligence Solutions ecosystem accelerates AI adoption for SMEs.
Across geographies and industries, AI-driven decisioning, optimization, and analytics are becoming crucial levers for resilience and growth. The Swisscard-FICO collaboration demonstrates how financial services players can harness AI to tailor customer experiences while retaining controls on risk. In mobility, the Ducati-V21L prototype hints at the pace of improvement in charging tech that could later permeate broader vehicle categories and energy networks. In health tech, AI-first thinking is redefining R&D, manufacturing, and safety protocols; in devices, AI-enabled minimally invasive tools promise to raise precision and outcomes. Huawei’s ecosystem strategy presents a model for scaling AI from the lab to the storefront—an essential step for SMEs that historically faced barriers to entry into the AI economy. Public safety and surveillance firms face a balancing act between innovation and privacy, requiring rigorous governance and privacy safeguards. And the software sector is rethinking pricing models to reflect ongoing AI updates and the value they deliver.
Looking ahead, the AI revolution is not a single technology push but a tapestry of interconnected systems that span finance, mobility, health, manufacturing, and security. The common thread is a shift toward data-driven decisioning that can adapt in real time, a push for governance that emphasizes safety and ethics without stifling experimentation, and a movement toward open, interoperable ecosystems that enable businesses of all sizes to participate in AI-enabled growth. While the road is not without challenges—privacy concerns, cybersecurity, regulatory complexity, and the need for transparent AI—from banks to bike makers to bio-pharma—the momentum is unmistakable. The industries that best navigate this transition will be those that couple technical capability with clear governance, strong partnerships, and a commitment to responsible innovation.