AI’s Next Frontier: Policy, Infrastructure, and Industry Alliances Redefine the Tech Landscape in 2025
Author: Editorial Team
From boardrooms to government halls, 2025’s AI narrative is no longer a single technology story but a tapestry of policy, infrastructure, and market strategy. As labs push the boundaries of machine learning, industry leaders warn of an emergent threat: AI-enabled cybercrime that could outpace traditional defenses. Meanwhile, hardware companies race to deliver faster, more energy-efficient accelerators, and cloud and data-center builders plan the next wave of capacity to meet surging demand. In this landscape, cross-border collaborations, regulatory debates, and ambitious industrial programs are converging to determine how quickly AI can be deployed, and at what cost in security and reliability. This feature synthesizes insights from developments across the technology ecosystem—from calls for stronger cybercrime laws to the emergence of modular AI development platforms, and from major hardware partnerships to the expanding footprint of AI infrastructure in accelerating economies.
Policy and security headlines are sharpening as experts call for a legal framework against AI-driven cybercrime. The Businessworld reporting underscores a growing urgency among industry leaders to strengthen laws and foster international cooperation to curb fraud, phishing, and other crimes powered by AI. The proposals range from clarifying accountability for AI-generated deception to setting minimum standards for data protection and incident reporting, and to creating cross-border information-sharing mechanisms that can speed up investigations. The debate comes as criminal networks exploit AI to craft highly personalized phishing messages, deepfakes, and synthetic identities. Advocates argue that without robust, harmonized regulations, the benefits of AI-enabled innovation could be eroded by escalating risks. Critics caution that laws must balance security with innovation, avoiding stifling experimentation or imposing schemas that hinder legitimate research and deployment. The overarching aim is to align policy with rapid technology cycles, ensuring that defenders, businesses, and consumers share a common framework.
Hundreds of development teams are turning to modular AI architectures that promise more reliable and scalable workflows. Hackernoon’s coverage of the MCP server updates highlights how structured outputs, elicitation techniques, and resource links are becoming integral to modern LLM operations. The movement toward modular stacks—where specialized components handle perception, reasoning, and output generation—allows developers to recombine capabilities quickly, test alternatives, and trace decisions more transparently. Early adopters report faster iteration cycles, improved reproducibility, and better integration with existing software ecosystems. While much of this content remains behind paywalls, the broader takeaway is clear: a modular, auditable approach is increasingly seen as essential to navigating the complex, heterogeneous landscape of AI tooling in 2025.

Illustration of modular AI workflows, reflecting the MCP-style stack of perception, reasoning, and output components.
MIPS, a company closely watched for its AI-enabled hardware, announced the appointment of Alan Li as Head of Business Development for China. Li’s track record in automotive, industrial, and communications infrastructure is expected to accelerate MIPS’ regional growth and partnerships as demand for edge AI accelerators expands across Asia. The move signals how hardware players are aligning with national and regional AI ambitions, reinforcing the trend toward coordinated, cross-border deployment of AI capabilities—from manufacturing floors to smart cities—and highlighting the importance of local partnerships in navigating regulatory and market landscapes.

Alan Li, newly appointed Head of Business Development for China at MIPS, signaling intensified regional AI hardware strategy.
Beyond the lab and the showroom floor, the science underlying AI and computation continues to be inspired by breakthroughs in fundamental physics. The Hindu’s report on extreme nuclear transients near black holes — where stars are stretched, torn, and violently energized as they approach event horizons — underscores how complex, high-energy phenomena demand sophisticated modeling and data analysis. While not an AI article per se, such science illustrates the scale and complexity that AI systems aim to model, simulate, and accelerate. The cross-pollination between astrophysics, quantum physics, and machine learning is helping to drive novel algorithms, improved simulations, and better understanding of information flow in chaotic systems.
Astrophysical simulations of extreme energy processes near black holes — a reminder of the complex data problems AI seeks to solve.
Hardware competition and collaboration remain at the heart of AI acceleration. One headline involves Nvidia’s potential collaboration with Samsung to advance AI chip technology and memory bandwidth through innovations like high-bandwidth memory (HBM) solutions. Another major strand is the partnership between Nvidia and Intel to co-develop multiple generations of custom datacenter and personal computing products, reflecting a broader strategy to diversify supply chains and ensure rapid deployment of AI workloads across enterprise and edge environments. These dynamics highlight how competitive pressures and strategic alliances are shaping the hardware stack that underpins modern AI—from GPUs to accelerators, memory, and system-integration capabilities.

NVIDIA and Samsung are advancing AI chip technology, signaling a new phase in AI hardware competition.
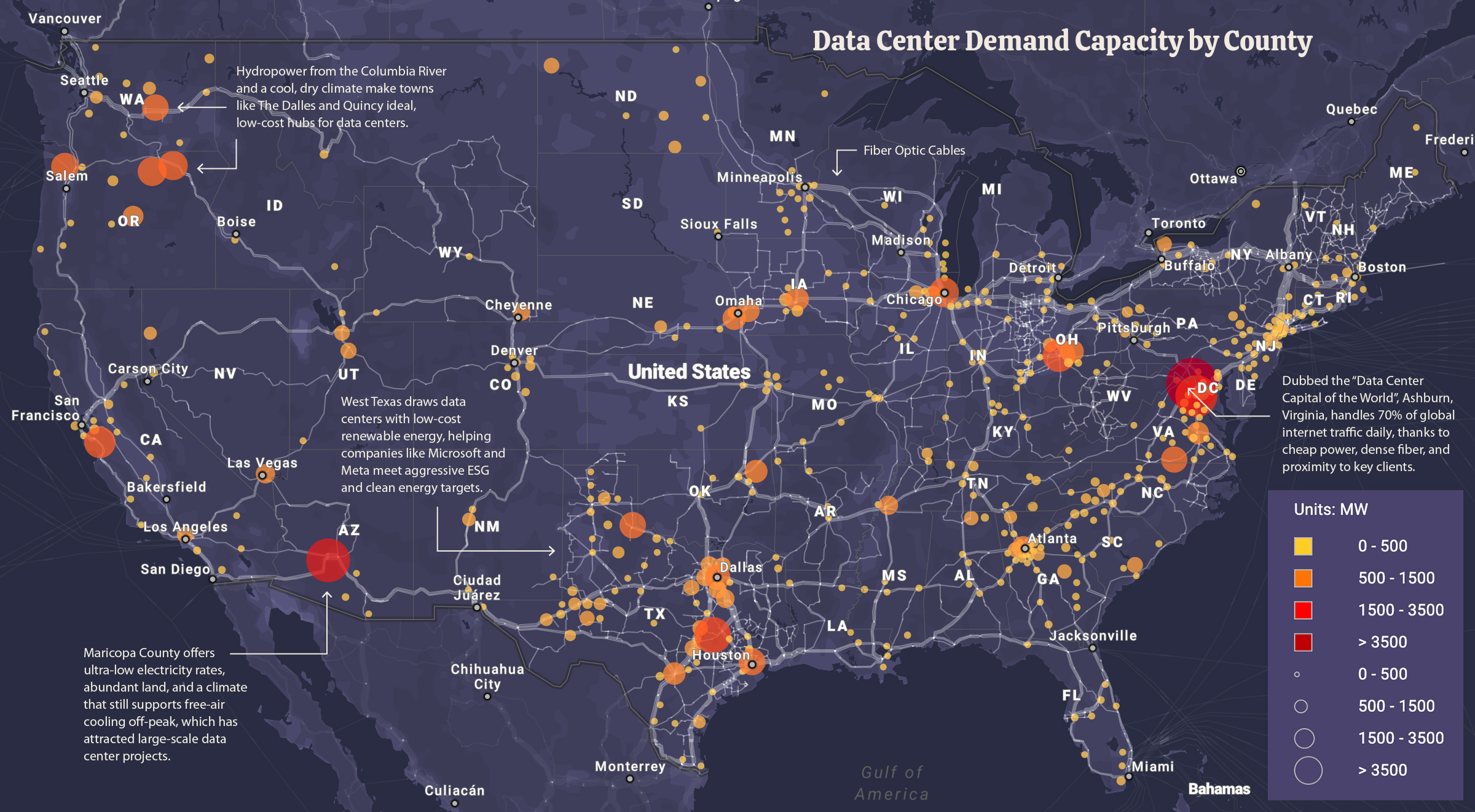
As organizations scale AI, data-center energy consumption has emerged as a critical constraint. Visual Capitalist’s data-center power map and related visualization, discussed in coverage of U.S. data-center energy use, highlights the enormous energy requirements behind modern AI. The information underscores the need for efficiency, wiser capacity planning, and smarter cooling, as data centers could see energy demand doubling by the end of this decade. The related analysis from FinancialContent aggregations also points to the geographic distribution of data-center activity and the strategic importance of location, grid reliability, and policy frameworks that incentivize clean energy and demand-response programs. In short, the infrastructure that makes AI possible is also demanding substantial electrical power, making energy efficiency a central competitive differentiator.

A map highlighting the sprawling energy footprint of data centers powering AI workloads in the United States.
The United Kingdom’s ambitious AI infrastructure push is another major inflection point, with reports suggesting that Microsoft and Amazon are among the primary beneficiaries. The UK government’s sizable investment—on the order of tens of billions—aims to accelerate the deployment of AI-ready infrastructure, data centers, and cloud capacity. For multinational cloud players, this represents a potential rebalancing of cloud economics and a chance to expand regional service capabilities. The development also suggests new opportunities for local AI startups and research institutions to collaborate with global technology giants, leveraging a more connected, data-rich environment to accelerate experimentation and deployment across sectors such as health care, finance, and manufacturing.

Illustrative map of AI-driven infrastructure development and data-center growth in the UK and Europe.
In the investment community, quantum computing remains a hot topic. The Fool’s discussion of three quantum computing stocks that could make a millionaire reflects the high-risk, high-reward nature of this frontier. While the technology promises exponential gains in solving certain classes of problems, investors should weigh valuation, execution risk, and the timeline for practical, large-scale quantum advantage. The broader takeaway is that quantum acceleration is increasingly considered part of the longer horizon for AI computing, with potential implications for optimization, materials science, cryptography, and beyond.

Quantum computing stocks capture investor imagination as AI workloads broaden into new computational paradigms.
The corporate AI-infrastructure landscape also features high-stakes collaborations among industry leaders. Global Legal Chronicle reports on NVIDIA and Intel’s collaboration to jointly develop multiple generations of custom datacenter and personal computing products, reflecting an enduring trend toward mega-deals and strategic alignments that aim to secure leadership across hardware, software, and services in AI ecosystems. Such alliances help diversify risk, accelerate product roadmaps, and standardize interfaces that enterprises rely on to deploy AI at scale.

Global Legal Chronicle coverage of a major NVIDIA–Intel collaboration on AI infrastructure.
Finally, the Indian AI market continues to garner attention from investors and builders alike. NetWeb Technologies’ reported fresh ₹450 crore order and bullish commentary from SEBI analysts signal strong momentum for AI-ready infrastructure providers in India. As AI workloads broaden from cloud data centers to regional campuses and edge deployments, local suppliers find opportunities in a rapidly expanding market with global demand. The Indian story complements the UK and US narratives, illustrating how AI-enabled growth is spreading across geographies with differing regulatory and market dynamics.

India’s AI infrastructure market gains traction as NetWeb Technologies secures a large order and analysts stay bullish.
As these threads weave together—policy safeguards, scalable modular AI architectures, strategic hardware partnerships, data-center growth, and expanding regional ecosystems—the 2025 tech landscape looks less like a single hype cycle and more like a coordinated effort to build robust, secure, and globally interconnected AI capabilities. The coming years will test whether all these pieces can align: regulations that deter misuse, hardware and software ecosystems that accelerate innovation, and energy and grid infrastructure capable of supporting a digital economy that relies on AI to drive productivity across industries.